تعرف على أكثر الأعضاء وزناً في جسمك
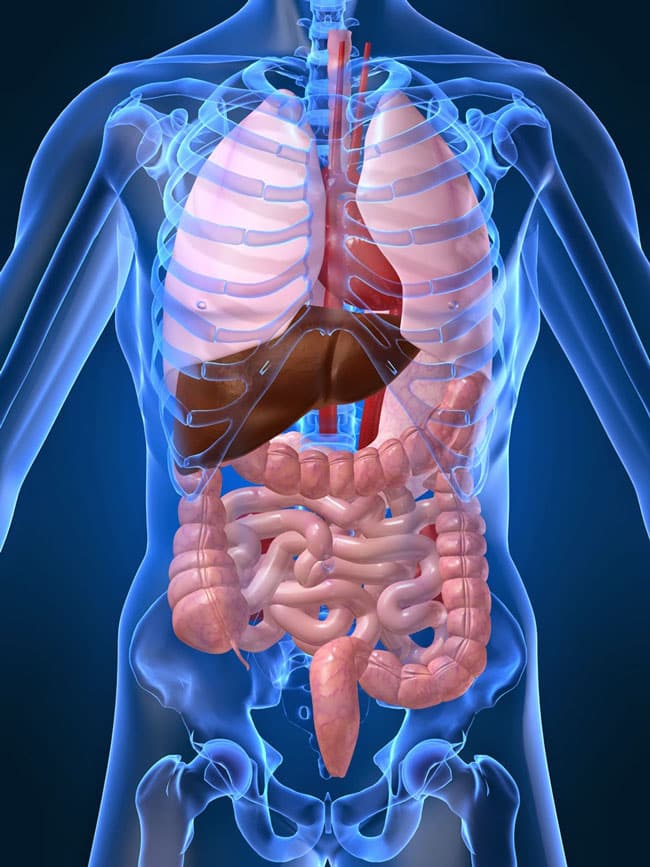
تعرف على أكثر الأعضاء وزناً في جسمك
تعرف على أكثر الأعضاء وزناً في جسمك
يتكون كل عضو من أعضاء جسم الإنسان من مجموعة من الأنسجة التي تعمل معاً لأداء مهمة محددة في الجسم، مثل هضم العناصر الغذائية أو إنتاج رُسُل كيميائية تُمكِّن خلايا الدماغ من التواصل. على الرغم من أن العلماء لديهم وجهات نظر مختلفة حول ما يمكن اعتباره عضواً بالضبط، فإن أكثر عدد تم الاستشهاد به من أعضاء في جسم الإنسان يبلغ 78 عضواً، بما يشمل الوحدات الوظيفية الرئيسية مثل الدماغ والقلب، بالإضافة إلى أجزاء الجسم الأصغر، مثل اللسان.
بحسب ما نشره موقع Live Science، تأتي أعضاء جسم الإنسان في جميع الأشكال والأحجام لتعكس عددا لا يحصى من الوظائف المهمة التي تؤديها. لكن أي من أعضاء الجسم يزن أكثر؟ ربما تتفاجأ عندما تعرف الإجابة على هذا السؤال، فيما يلي:
الجلد
يرتدي الجلد تاج أثقل عضو في جسم الإنسان، لكن يوجد بعض التناقض في مقدار وزنه بالفعل. تشير بعض المصادر إلى أن البالغين يحملون ما متوسطه 3.6 كيلوغرام من الجلد، بينما تقول مصادر أخرى إن الجلد يشكل حوالي 16% من إجمالي وزن الجسم للبالغين، وفي هذه الحالة إذا كان وزن الشخص 77 كلغ على سبيل المثال، فسيزن جلده حوالي 12.3 كلغ.
ووفقاً لتقرير صدر عام 1949 في دورية الأمراض الجلدية الاستقصائية، فإن التقدير الأكبر يحسب السبلة الشحمية، وهي طبقة من الأنسجة الدهنية تقع بين الطبقات العليا من الجلد والعضلة الكامنة، كجزء من الجلد، بينما يتم احتساب هذه الطبقة النسيجية منفصلة في التقديرات الأقل وزناً.
يجادل باحثو التقرير ضد إدراج السبلة الشحمية وبالتالي يستنتجون أن الجلد لا يشكل سوى حوالي 6% من وزن الشخص البالغ. لكن نصاً مرجعياً طبياً حديثاً، وهو Primary Care Notebook، ينص على أن الأنسجة الدهنية هي جزء من الطبقة الثالثة والأعمق من الجلد، اللحمة، مما يشير إلى ضرورة احتسابها.
عظم الفخذ
يعتبر الهيكل العظمي نظاماً عضوياً، أو مجموعة من الأعضاء تؤدي معاً وظائف فسيولوجية محددة. يعد الهيكل العظمي أحد أكبر أنظمة الأعضاء في جسم الإنسان، ويمكن أن يصل وزنه إلى ما يقرب من 15% من إجمالي وزن جسم الشخص البالغ، وفقاً لمراجعة نُشرت عام 2019 في الدورية الدولية للعلوم البيولوجية.
يحتوي الهيكل العظمي البالغ عادة على 206 عظمة، على الرغم من أن بعض الأفراد قد يكون لديهم أضلاع أو فقرات إضافية. يقع عظم الفخذ بين الركبة والورك، هو الأثقل منها جميعاً. في المتوسط، يزن عظم الفخذ حوالي 380 غراماً، لكن وزنه الدقيق يختلف باختلاف العمر والجنس والحالة الصحية.
الكبد
وفقاً لمؤسسة الكبد الأميركية، يزن الكبد حوالي 1.4 إلى 1.6 كلغ، وهو ثاني أثقل عضو في جسم الإنسان. إن الكبد عبارة عن عضو مخروطي الشكل يقع أعلى المعدة وتحت الحجاب الحاجز، وهو عبارة عن عضلة على شكل قبة تقع تحت الرئتين. يساعد الكبد على تكسير السموم وهضم الطعام، من بين وظائف حيوية أخرى. وفقاً لجونز هوبكنز ميديسن، يحتفظ الكبد طوال الوقت بحوالي نصف لتر من الدم، أي حوالي 13% من إمداد الجسم بالدم.
الدماغ
من التفكير إلى التحكم في الحركة، يؤدي الدماغ البشري عدداً لا يحصى من الوظائف الحيوية في الجسم، ويعكس وزنه أهميته. وفقاً لتعليق نُشر في دورية PNAS، يمثل الدماغ حوالي 2% من متوسط وزن جسم الإنسان البالغ.
يعتمد وزن كتلة الدماغ أيضاً على عمر الشخص وجنسه. في سن العشرين، يزن دماغ الرجل 1.4 كلغ. في سن 65، ينخفض إلى 1.3 كلغ. وفقاً لموسوعة الدماغ البشري الأكاديمية، يبلغ وزن أدمغة الإناث حوالي 10% أقل من عقول الذكور، لكن بحسب ما نشرته دورية Intelligence، فإنه عند أخذ وزن الجسم الإجمالي في الاعتبار، تميل أدمغة الرجال إلى أن تكون أثقل بمقدار 100 غم فقط.
الرئة
تعتبر الرئتين من أعضاء جسم الإنسان الثقيلة الوزن. تزن الرئة اليمنى عادةً حوالي 0.6 كلغ، بينما تكون الرئة اليسرى أصغر قليلاً وتزن حوالي 0.56 كلغ. كما تكون رئتا الذكور البالغين أثقل من الإناث.
ومن المثير للاهتمام أن الرئتين تزنان 40 غراما عند الولادة. تتطور الرئتان بشكل كامل فقط عندما تتشكل الحويصلات التنفسية في سن الثانية، عندها تزن الرئتان حوالي 170 غراما.
القلب
يقع قلب الإنسان في مركز الدورة الدموية ويضخ الدم بلا كلل عبر الجسم، ويرسل الأكسجين والمواد المغذية إلى الأنسجة. تشكل الألياف العضلية الثقيلة التي تحرك ضربات القلب معظم وزنه. يزن القلب حوالي 280 إلى 340 غراما في الذكور البالغين وحوالي 230 إلى 280 غراما في الإناث البالغات.
الكلى
تتخلص الكلى من سموم وفضلات الجسم. تتم هذه المهمة المحورية عن طريق النيفرون، وهي هياكل صغيرة تعمل كمرشحات بين مجرى الدم والمثانة. تحتوي كل كلية على ملايين النيفرون، مما يجعل هذا العضو الحيوي واحداً من أعضاء الجسم الثقيلة الوزن. يبلغ وزنها بين حوالي 125 إلى 170 غراما عند الذكور البالغين ومن 115 إلى 155 غراما لدى الإناث البالغات.
الطحال
يقع الطحال على مقربة من البنكرياس، حيث يزيل خلايا الدم الحمراء القديمة والتالفة من مجرى الدم، وينظم مستويات الدورة الدموية لخلايا الدم البيضاء، وينتج أجساماً مضادة وجزيئات مناعية تساعد في مكافحة العدوى. يزن الطحال في المتوسط 150 غراماً عند البالغين، لكن وفقاً لمراجعة علمية في عام 2019 نُشرت في دورية Surgery، يختلف الوزن من شخص لأخر.
البنكرياس
ينظم البنكرياس مستويات السكر في الدم ويفرز الإنزيمات التي تساعد الأمعاء على امتصاص العناصر الغذائية من الطعام المهضوم. إلى جانب الطحال، يعتبر البنكرياس من أعضاء الجهاز الهضمي ثقيلة الوزن. يزن البنكرياس عادةً من 60 إلى 100 غرام عند البالغين. ويمكن أن يصل وزنه إلى 180 غراما لدى بعض الأفراد.
الغدة الدرقية
توجد الغدة الدرقية في الرقبة وتلعب دوراً رئيسياً في تنظيم استخدام الجسم للطاقة. يختلف وزنها بين الأفراد، لكنها عادة ما تزن حوالي 30 غراما. قد تصبح الغدة الدرقية أثقل أثناء الحيض والحمل. يمكن أن يؤدي فرط نشاط الغدة الدرقية، وهي حالة طبية تؤدي إلى إنتاج الغدة الدرقية للهرمونات أكثر مما يحتاجه الجسم، إلى نموها وزيادة حجمها.
غدة البروستاتا
على الرغم من صغر حجمها نسبياً، والذي يمكن مقارنته بحجم الجوز، فإن البروستاتا هي واحدة من أعضاء جسم الإنسان الثقيلة الوزن. يبلغ متوسط وزن البروستاتا عند البالغين حوالي 25 غراما، ولكن قد يختلف وزنها من شخص لآخر. وفقاً لجامعة يوتا، يمكن أن تنمو البروستاتا المتضخمة إلى أكثر من ثلاثة أضعاف متوسط الحجم والوزن لتصل إلى حوالي 80 غراما.






