A dangerous discovery that changes the course of heart attacks
A dangerous discovery that changes the course of heart attacks
A dangerous discovery that changes the course of heart attacks
Acute inflammation, whether it's redness, pain, or bruising around an injury, is a way of alerting the immune system to damage that needs to heal.
But, if the immune response persists for too long, chronic inflammation can lead to attack on healthy tissues and the risk of developing serious disease increases increasingly.
In a recent study, a team of researchers in Australia made a startling discovery, revealing how white blood cells move from blood vessels to infection sites, a discovery that will open the door to developing treatments that can stop or slow down the transmission of white blood cells in their tracks, thus saving Better outcomes for diseases caused by chronic inflammation.
"breakaway" mechanism
The study, conducted by the Centenary Institute of Cancer Medicine and Cell Biology in Australia, also revealed the mechanism by which neutrophils "detach" from blood vessels, allowing them to move around the body. Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell that are essential components of the immune system and the “first responder” to injury or infection, but too much of a good thing over time can lead to chronic and dangerous inflammatory conditions, according to New Atlas.
PDI protein
Dr Joyce Chiu, lead researcher of the study from the Centenary Research Center at the University of Sydney, said that to move to the site of infection, neutrophils must attach to and detach from the walls of blood vessels, and that although it is known how integrins help neutrophils stick together, But it was not known how to break up.”
The scientists identified a protein secreted by neutrophils, protein disulfide isomerase PDI, that plays a pivotal role in enabling cells to separate from blood vessels, and which Dr. Chiu believes by targeting neutrophil release could be limited.
New drugs
She also added: "New drugs could be designed to inhibit PDI, to prevent neutrophils from 'unbinding' and migrating from the walls of blood vessels. Preventing neutrophils from moving around can help prevent chronic inflammation by reducing their ability to accumulate at sites of injury or infection.”
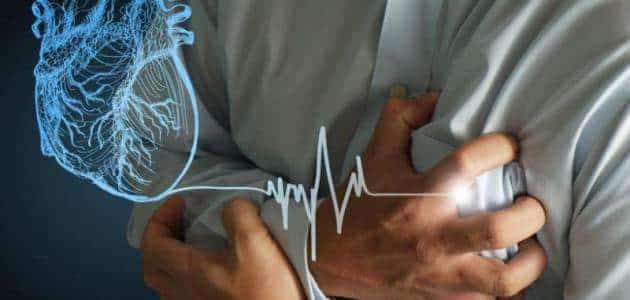
Heart attacks and strokes
While neutrophils are, of course, essential for the immune response to injury, reducing their ability to collect and damage healthy tissue probably has a major impact on chronic inflammatory-related diseases such as heart attack and stroke.
“The research findings could pave the way for new therapies and management strategies that are able to reduce the extent of inflammation, and potentially improve outcomes for individuals with chronic inflammatory and cardiovascular disease,” said Dr. Chiu.